
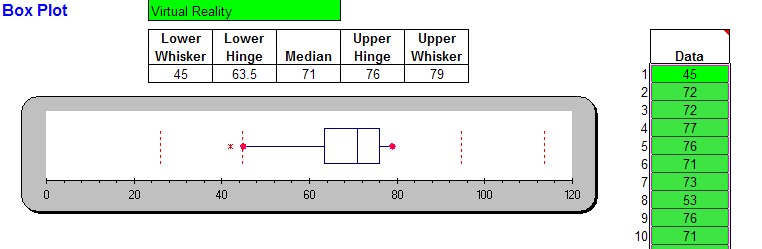
That is, the rectangular bars(or boxes), top of the boxes indicating the upper quartile, the bottom of the boxes indicating the lower. The name, box and whisker plot is derived from the nature of the graph. It may also have line extensions extending from the boxes, which usually indicates variability beyond the upper and lower quartiles. With a loose definition of outliers, you could use the chart to identify the possible existence. A box plot is a statistical data visualization technique that uses rectangular bars to indicate data groups through their quartiles. The interpretation of the compactness or spread of the data also applies to each of the 4 sections of the box plot. If the box plot is relatively tall, then the data is spread out. To get started, you need a set of data to work with. IF the box plot is relatively short, then the data is more compact. A box plot is a good way to get an overall picture of the data set in a compact manner. First, let us look at a very simple example. The box-whisker plot (or a boxplot) is a quick and easy way to visualize complex data where you have multiple samples. Box plots are used to show overall patterns of response for a group. Interpreting box plots/Box plots in general.
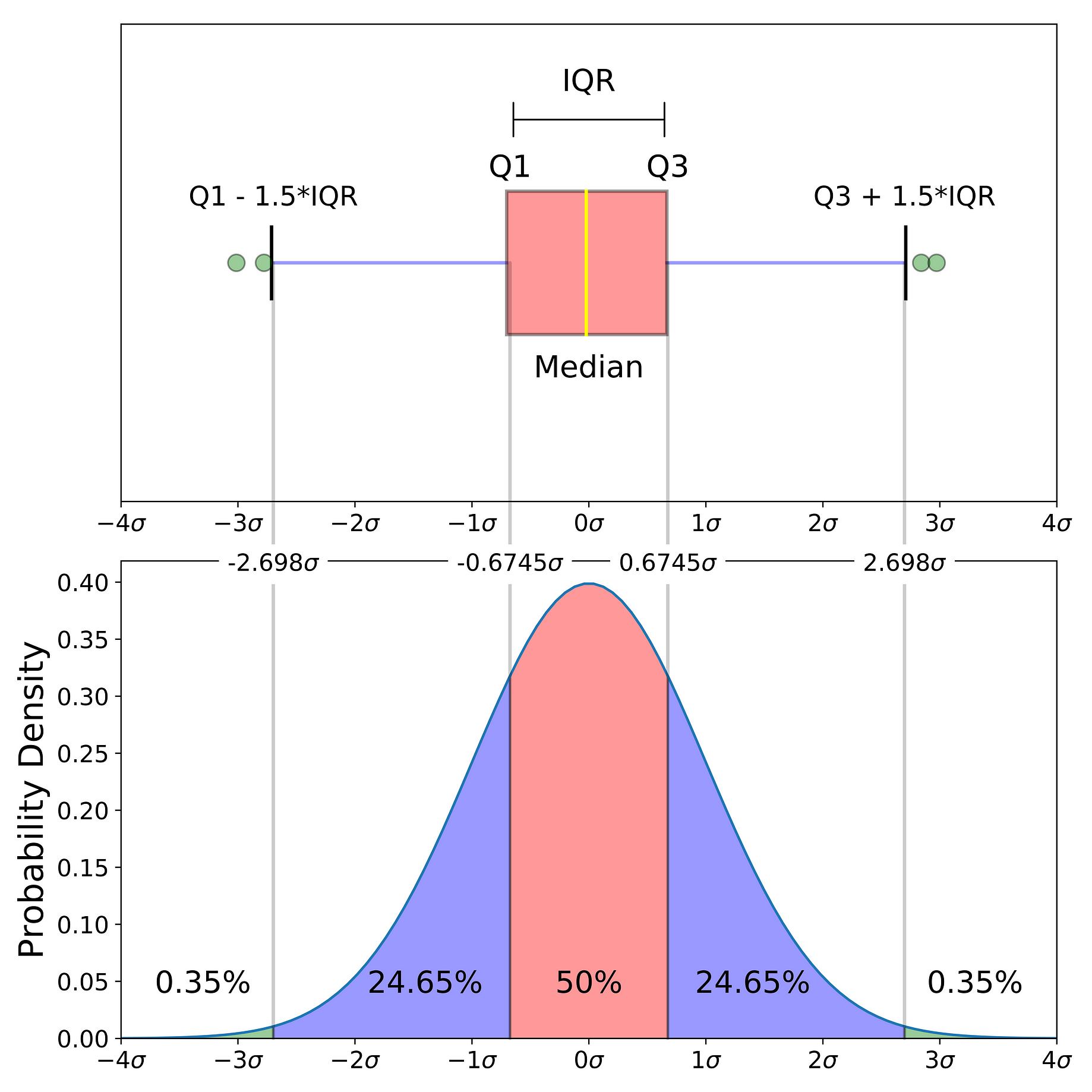
Whiskers often (but not always) stretch over a wider range of scores than the middle quartile groups.
Box and whisker plot definition how to#
Discusses quartiles and medians, shows how to find them, and explains how they relate to box-and-whisker plots. Whiskers The upper and lower whiskers represent scores outside the middle 50. You can create a BOX Plot in SAS using the SG PLOT procedure. Explains how to construct a simple box-and-whisker plot, and demonstrates the steps. Q1 – 1.5 * IQR How to create a Box and Whisker plot in SAS? Similarly, if a value is lower than the 1.5*IQR below the lower quartile (Q1), the value will be considered an outlier. Outlier: If a data point is higher than the 1.5*IQR above the upper quartile (Q3), the value will be considered an outlier. Interquartile range (IQR): It is the box plot showing the middle 50% of scores and can be calculated by subtracting the lower quartile from the upper quartile (e.g. Negatively Skewed: When the median is closer to the upper quartile (Q3) and the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the box, then the distribution is negatively skewed. Box and whisker plot charts display data values in quartiles and are used to depict information from related data sets with independent sources. If you check the fence option then gate values will be calculated automatically. Positively Skewed: When the median is closer to the lower or bottom quartile (Q1) then the distribution is positively skewed. This form of box and whisker plot is often used to represent outliers. Normal Distribution or Symmetric Distribution: If a box plot has equal proportions around the median and the whiskers are the same on both sides of the box then the distribution is normal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
